Unfortunately, electric shocks remain one of the least-understood symptoms of menopause. Although more research is needed to truly pinpoint the source of these electrical sensations in the head and body, it's important to learn all there is to know about current possible causes so that you can get a treatment plan underway.
About Feelings of Electric Shock
Some women describe electric shocks as similar to a rubber band snapping between muscles. Others call it a “zap” within the nerves of their head or extremities or across the skin, such as when a limb goes numb.
The immediate trigger for electric shocks is a “misfiring” in the process of brain and nerve cell communication in structures known as electrical synapse. This process involves passing incredibly rapid electrical signals to the immediately adjacent cell, and is usually responsible for rapid defensive reflexes.
If these electric signals go amiss, they can produce these “zapping” sensations in the limbs. There are varying underlying causes for these error.
Causes of Electric Shock Sensations
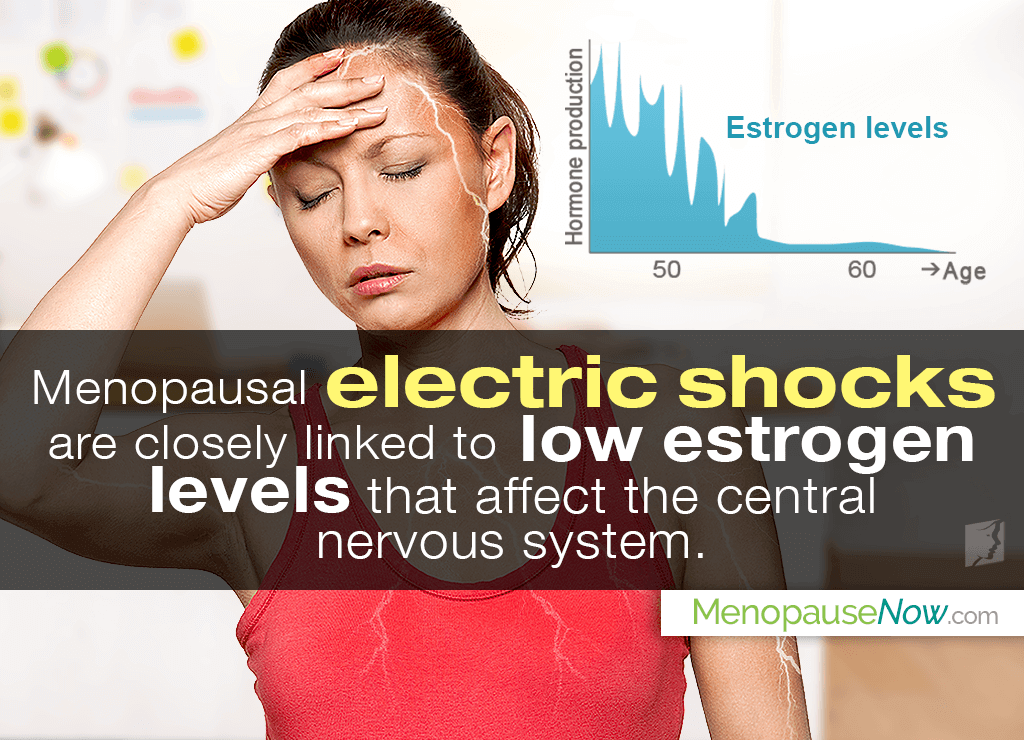
Many researchers believe that menopausal electric shocks are closely linked to low estrogen levels that affect the central nervous system, increasing a woman's propensity to suffer from synapse misfiring and, thus, electric shock feelings in the head and body.
Other causes of electric shock sensations include:
- Hot flashes. Though hot flashes are not a direct cause, many women report feelings of electric shock immediately preceding a hot flash, leading experts to believe that a connection between the two is highly likely. Hot flashes also stem from low estrogen levels.
- Osteoporosis. Women suffering from osteoporosis may be more prone to electric sensations in the body as the loss in bone density could damage the nerves within the spine.
Coping with Electric Shock in Head and Body
Fortunately, the following tips can help you find relief from these uncomfortable sensations:
- Relax. High stress levels cause a buildup of cortisol, a hormone that can increase your chances of electric shocks. Give yourself at least half an hour a day to destress by meditating, doing breathing exercises, partaking in a favorite hobby, etc.
- Improve your diet. Calcium is important for proper synaptic function and bone health, while vitamin D is necessary for proper calcium absorption. Also, a lack of vitamins B12 and E as well as potassium, magnesium, and omega-3 fatty acids have all been linked to more frequent electric shocks.
- Review your medications. If you are experiencing this sensation as a result of prescription drugs, talk to your doctor about reducing the dosage or switching medications.
- Consider herbal supplements. Some alternative treatments contain plant estrogens to help raise estrogen levels - like phytoestrogenic herbal supplements containing dong quai, black cohosh, etc. - or work with your body to nourish endocrine glands for optimal hormonal health, such as the hormone-regulating supplement Macafem.
Understanding the possible causes of electric shocks in the head and body is the first step towards finding relief. If you suffer from this condition, talk to your doctor to find out if electric shocks are a symptom of a larger issue, and together, you can make a plan for managing discomfort that will work for you.
Click on the following link to learn more about natural and effective electric shock sensation treatments that will bring you relief not only from electric shock feelings in the head and body, but also other menopause symptoms that may be plaguing your days.
Sources
- National Osteoporosis Foundation. (n.d.). Symptoms, Risk Factors & Complications | Calcium/ Vitamin D. Retrieved May 27, 2019, from https://www.nof.org/pagets-symptoms/ | https://www.nof.org/patients/treatment/calciumvitamin-d/
- Simpson, K.R. & Bredesen, D.E. (2006). The Perimenopause and Menopause Workbook. California: New Harbinger Publications. Available from Google Books.